| .. | ||
| img | ||
| README.org | ||
- Overview
- Subscriber Plans
- Topologies
- Routing Protocols
- Underlying framing
- Tries
- Transport Technologies
- Test tools
- Congestion Controls
- Diffserv Markings
- Failure Modes
Overview
Setting up 4 simulation environments is in order:
| Plan Size | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Small | 1024 users |
| Medium | 10000 users |
| Large | 40000 users |
| Humongous | 100k users |
IP address ranges
2001:0002::/48 and 198.18.0.0/15 are the experimental address ranges. For testing outside of the network, perhaps a BGP AS for this would help
DNS service
nsupdate for reverse dns? Hosts file?
Subscriber Plans
| Plan Type | Down | Up | MinDown | MinUP | Cap | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OldDSL | 4Mbit | 384kbit | 1Mbit | |||||
| OldDSL6 | 6Mbit | 1Mbit | 3Mbit | |||||
| Cable20 | 20Mbit | 4Mbit | 12mbit | |||||
| LifeLine | 25Mbit | 3Mbit | ||||||
| FCCmin | 25Mbit | 3Mbit | ||||||
| NTIAserved | 100MBit | 20Mbit | 20Mbit | 5Mbit | ||||
| Biz50 | 50MBit | 20Mbit | 50Mbit | 20Mbit | ||||
| Biz100 | 100MBit | 100Mbit | 100Mbit | 100Mbit | ||||
| Biz200 | 200Mbit | 20Mbit | 200Mbit | 20Mbit | ||||
| Biz500 | 500Mbit | 50Mbit | ||||||
| Sym1000 | 1Gbit | 1Gbit | ||||||
| Sym100 | 100Mbit | 100Mbit | ||||||
| Sym10 | 10Mbit | 10Mbit |
Topologies
A variety of topologies need to be emulated.
Distance
Hops
Different technologies
Routing Protocols
Both ISIS and OSPF are in use
Underlying framing
PPPoe, MPLS are in use CGNATs might become an issue IPv6 deploying?
Tries
Some customers (particularly business ones) have multiple IP addresses. Everyone, using IPv6, has multiple IP addresses.
Worse, these are often dynamic in origin.
Transport Technologies
| Plan | Down | Up | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WiFi | ||||||||
| Cable | 2ms | 6ms | ||||||
| Docsis LL | 1ms | |||||||
| Wireless half duplex |
Test tools
Flent
TRex
goresponsiveness
crusader
speedtest.net
Web PLT
Alexa top 10000
samknows
Netflix video quality
VOIP MOS
Videoconferencing Quality
Congestion Controls
| Control | Why | ecn | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cubic | Linux | S | ||
| reno | BSD | S | ||
| ledbat | Torrent | N | ||
| ledbat++ | Microsoft | Y | ||
| curved | Microsoft | S | ||
| bbr | N | |||
| bbrv2 | Google exp | L | ||
| prague | IETF exp | L |
Diffserv Markings
EF,LE,CS1, CS5,NQB,CS6
Failure Modes
AQM
fq_codel was not designed to be a middlebox. The FQ component works well, the AQM component, doesn't work as well as it could.

Putting cake on the CPE also results in a metric ton less jitter.
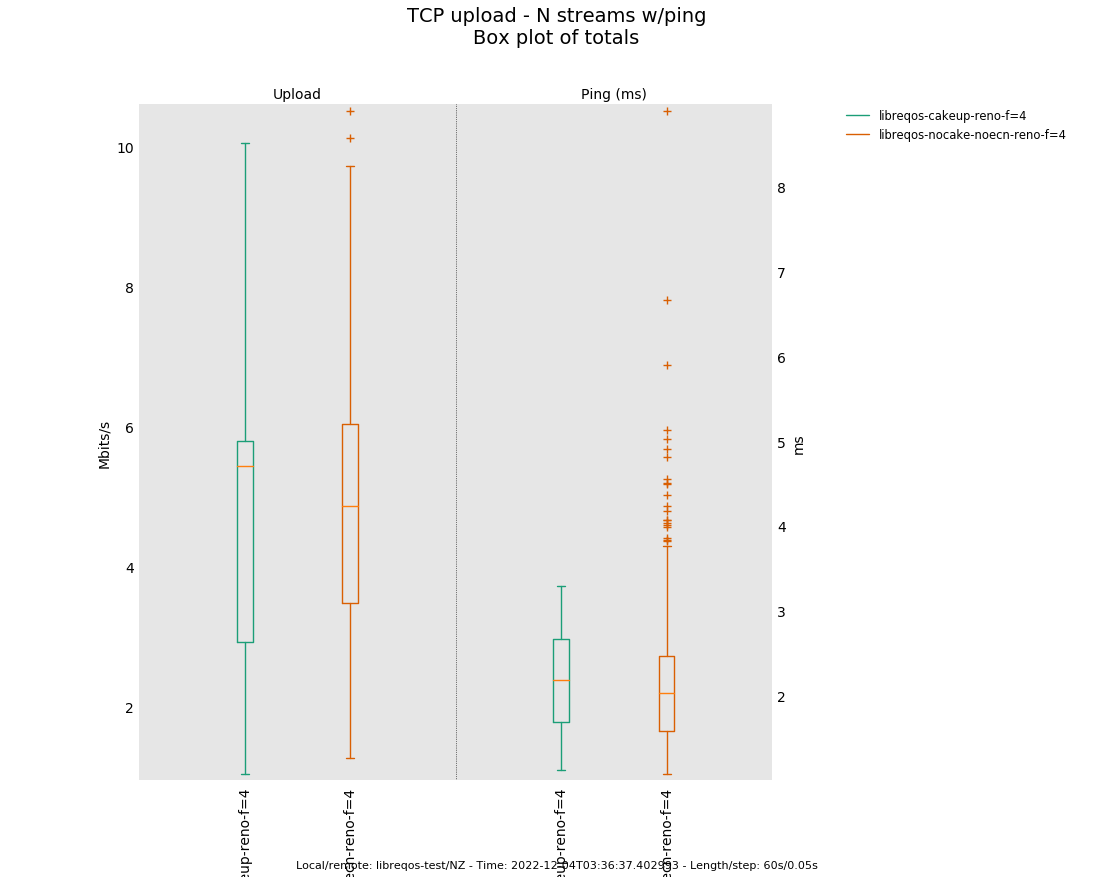
Similarly, many devices are themselves the bottleneck, still, so they accumulate a ton of RTT themselves, and monitoring the RTT and doing something about it would possibly help.
Validating the the RTT metrics reported by pping line up with the actual measurements from actual flows is important. Also, what are the effects of ack-filtering on pping?
FQ
The FQ methods we use are really good for most traffic types, and could be even better if more applications did single packet pacing and were more sensitive to delay and jitter.
Encapsulations
We have no insight into QUIC or VPN traffic. This is going to get worse over time. The only thing we have for quic is the: spin bit - which is probably not widely implemented. The best insight we actually have is queue accomulation and packet drop/mark behaviors.
HTB is bursty
DSCP
What DSCPs are in common use today?
DROP_MONITOR
We have 2600 (not kidding, 2600) places where packets can be dropped in the kernel, not to mention other parts of the network. A nice feature would be to be able to track retransmits relative to drops.