There was previously an issue where during the partial reload, LibreQoS.py would fail to parse the network structure correctly. Now resolved. |
||
|---|---|---|
| .github | ||
| docs | ||
| v0.7 | ||
| v0.8 | ||
| v0.9 | ||
| v1.0 | ||
| v1.1 | ||
| v1.2 | ||
| v1.3 | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .gitmodules | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
LibreQoS is a Quality of Experience (QoE) Smart Queue Management (SQM) system designed for Internet Service Providers to optimize the flow of their network traffic and thus reduce bufferbloat, keep the network responsive, and improve the end-user experience.
Servers running LibreQoS can shape traffic for many thousands of customers.
Learn more at LibreQoS.io!
Features
Flexible Hierarchical Shaping / Back-Haul Congestion Mitigation
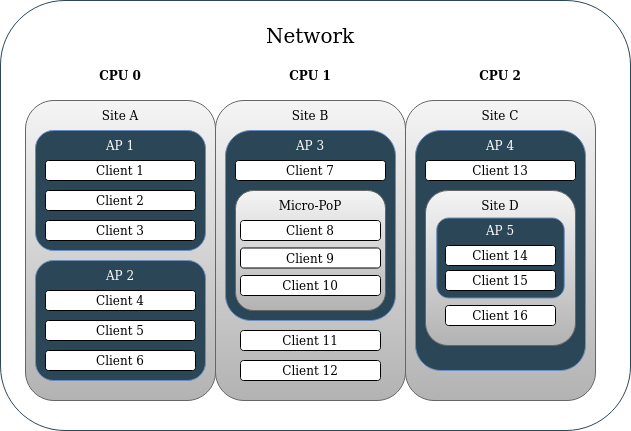
Your network hierarchy is mapped to a json file. This allows for both simple network hierarchies (Site>AP>Client) as well as much more complex ones (Site>Site>Micro-PoP>AP>Site>AP>Client). This allows operators to ensure a given site’s peak bandwidth will not exceed the capacity of its back-haul links (back-haul congestion control). This can allow operators to support more users on the same network equipment with LibreQoS than with competing QoE solutions which only shape by AP and Client. Shaping just by AP and client could allow for high aggregate peaks to occur on back-hauls' links, which can trigger packet loss and disrupt network connectivity. LibreQoS’s flexible shaping provides a solution to this.
CAKE
CAKE is the product of a decade of development efforts to improve on fq_codel. With the diffserv4 parameter enabled – CAKE groups traffic into Bulk, Best Effort, Video, and Voice "tins" that closely match the relevant IETF diffserv standards (RFC4594, RFC7567, and RFC8622). This means that without having to fine-tune traffic priorities as you would with DPI products – CAKE automatically ensures your clients’ OS update downloads will not disrupt their zoom calls. It allows for multiple video conferences to operate on the same connection which might otherwise “fight” for upload bandwidth causing call disruptions.
XDP
Fast, multi-CPU queueing leveraging xdp-cpumap-tc. Currently tested in the real world past 11 Gbps (so far) with just 30% CPU use on a 16 core Intel Xeon Gold 6254. It's likely capable of 30Gbps or more.
Graphing
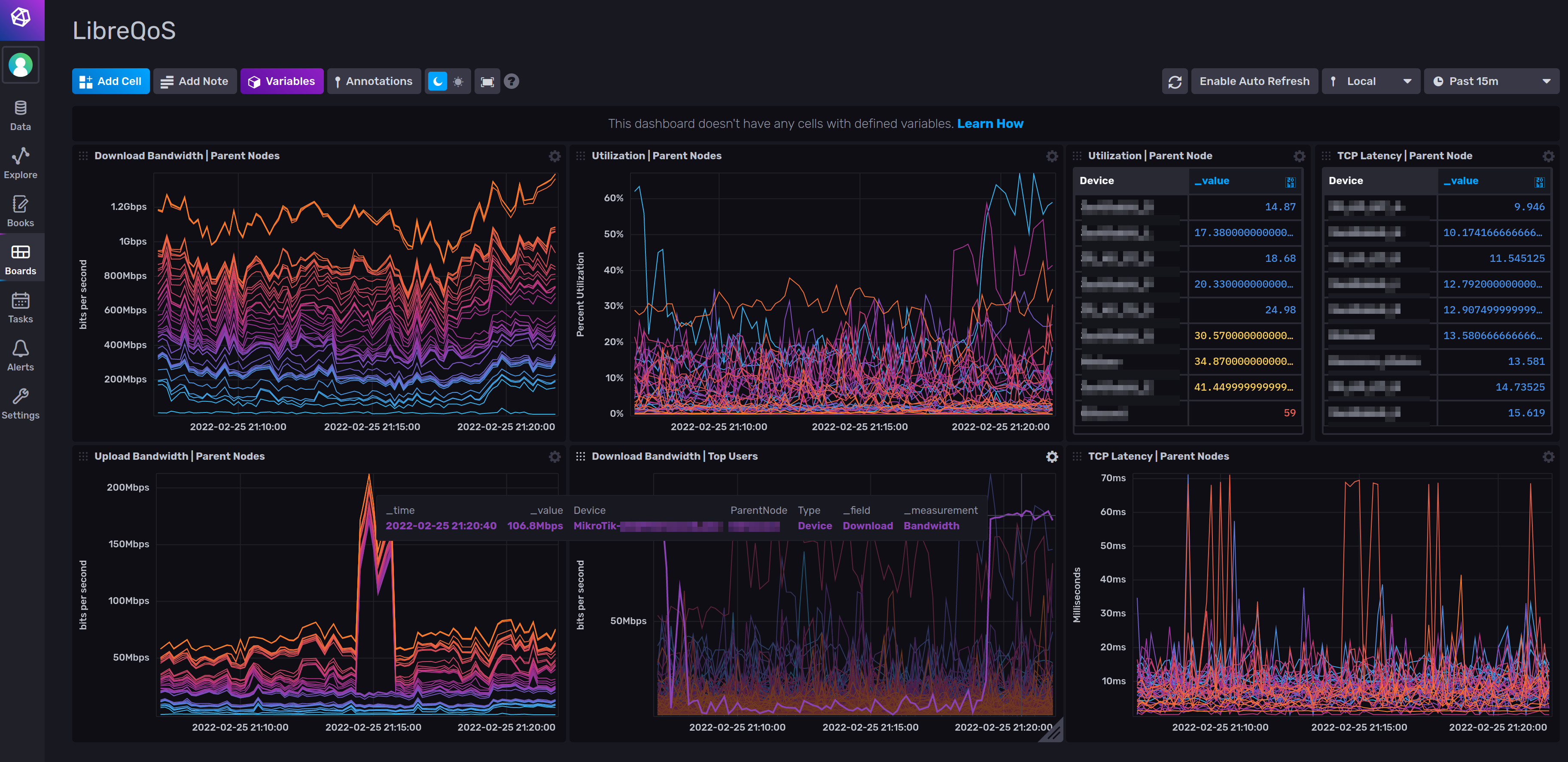
You can graph bandwidth by client and node (Site, AP, etc), with great visalizations made possible by InfluxDB.
CRM Integrations
- UISP
- Splynx
System Requirements
VM or physical server
- For VMs, NIC passthrough is required for optimal throughput and latency (XDP vs generic XDP). Using Virtio / bridging is much slower than NIC passthrough. Virtio / bridging should not be used for large amounts of traffic.
CPU
- 2 or more CPU cores
- A CPU with solid single-thread performance within your budget.
- For 10G+ throughput on a budget, consider the AMD Ryzen 9 5900X or Intel Core i7-12700KF
- CPU Core count required assuming single thread performance of 2700 or more:
| Throughput | CPU Cores |
|---|---|
| 500 Mbps | 2 |
| 1 Gbps | 4 |
| 5 Gbps | 8 |
| 10 Gbps | 12 |
| 20 Gbps* | 16 |
| 50 Gbps* | 32 |
| 100 Gbps* | 64 |
(* Estimated)
Memory
- Mimumum RAM = 2 + (0.002 x Subscriber Count) GB
- Recommended RAM:
| Subscribers | RAM |
|---|---|
| 100 | 4 GB |
| 1,000 | 8 GB |
| 5,000 | 16 GB |
| 10,000* | 32 GB |
| 50,000* | 48 GB |
(* Estimated)
Network Interface Requirements
- One management network interface completely separate from the traffic shaping interfaces. Usually this would be the Ethernet interface built in to the motherboard.
- Dedicated Network Interface Card for Shaping Interfaces
- NIC must have 2 or more interfaces for traffic shaping.
- NIC must have multiple TX/RX transmit queues. Here's how to check from the command line.
- Known supported cards:
- NVIDIA Mellanox MCX512A-ACAT
- Intel X710
- Intel X520
