fix(xosan): multiple sentences fixes
This commit is contained in:
@@ -10,21 +10,21 @@ This documentation will give you some advices and assistance in order to create
|
||||
|
||||
## Objectives
|
||||
|
||||
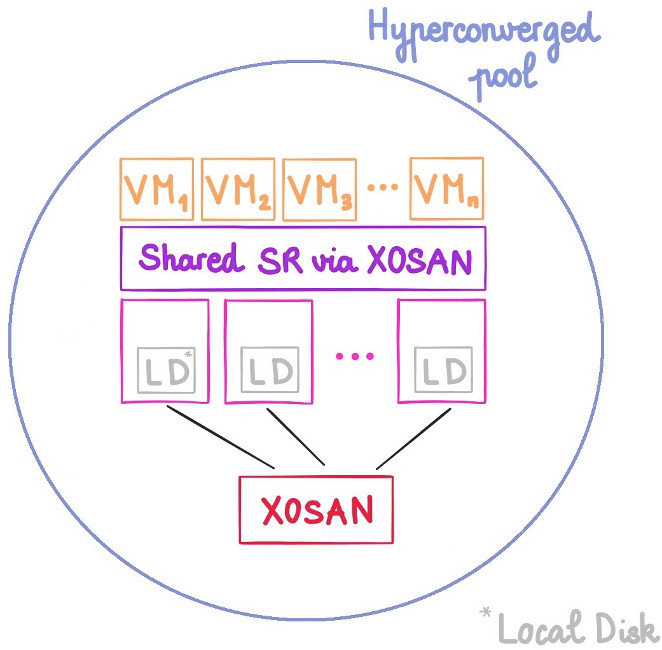
XOSAN will "gather" all your local disks into a shared SR, that XenServer will just see as any othershared SR, without limitations on it (you can live migrate, snapshot, backup, whatever you need). **It's a fully software solution** that doesn't require to buy extra-hardware. It could even run on the disk where your XenServer is already installed!
|
||||
XOSAN will "gather" all your local disks into a shared SR, that XenServer will just see as any other shared SR, without limitations on it (you can live migrate, snapshot, backup, whatever you need). **It's a fully software defined solution** that doesn't require to buy extra-hardware. It could even run on the disk where your XenServer is already installed!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The objectives are to:
|
||||
|
||||
* protect your data thanks to replication of data on multiple hosts
|
||||
* provide XenServer high availability without buying a NAS or a SAN
|
||||
* provide XenServer high availability without buying a NAS nor a SAN
|
||||
* give you flexibility to grow your storage by adding new nodes
|
||||
* work on all kind of hardware, from HDDs to SSDs
|
||||
* work on all kind of hardware, from HDDs to SSDs, with hardware RAID or not
|
||||
|
||||
## Beta access - Phase II
|
||||
|
||||
XOSAN is currently in beta phase II. Every user can access this beta stage and try the solution in its current version.
|
||||
To activate you XOSAN beta, just go in the **"XOSAN"** menu in your (up-to-date) XOA. Once on the menu, click on **"Register for Beta"**.
|
||||
XOSAN is currently in beta phase II. Every user can access this beta stage and try the solution in its current version.
|
||||
To activate you XOSAN beta, just go in the **"XOSAN"** menu in your (up-to-date) XOA. Once on the menu, click on **"Register for Beta"**.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
## Disperse type
|
||||
|
||||
Data are chunked and dispered on multiple nodes. There is a kind of "parity" data allowing to lost one or mode nodes ("like" RAID 5 or RAID 6).
|
||||
Data are **chunked and dispersed** on multiple nodes. There is a kind of "parity" data allowing to lost one or mode nodes ("like" RAID5 or RAID6).
|
||||
|
||||
Pros:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ Cons:
|
||||
|
||||
### Disperse 3
|
||||
|
||||
This is similar to **RAID 5**: there is an [algorithm](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reed%E2%80%93Solomon_error_correction) that will generate a kind of parity, being able to continue to work even if 1 node is down. If you reintroduce the node, it will be "healed" automatically.
|
||||
This is similar to **RAID5**: there is an [algorithm](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reed%E2%80%93Solomon_error_correction) that will generate a kind of parity, being able to continue to work even if 1 node is down. If you reintroduce the node, it will be "healed" automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
![picture disperse 3]()
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ If you lose one node, your data are still here. This mode will give you **66% of
|
||||
|
||||
### Disperse 5
|
||||
|
||||
Same than 3, like **RAID 5**, you can lose 1 node without service interruption.
|
||||
Same than 3, like **RAID5**, you can lose 1 node without service interruption.
|
||||
|
||||
![picture disperse 5]()
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -34,13 +34,13 @@ In this case, you'll be able to use up to **80%** of your total storage capacity
|
||||
|
||||
### Disperse 6
|
||||
|
||||
It's very similar to **RAID 6**. You can lose up to 2 nodes, it will continue to work in read and write.
|
||||
It's very similar to **RAID6**. You can lose up to 2 nodes, it will continue to work in read and write.
|
||||
|
||||
![picture disperse 6]()
|
||||
|
||||
## Growing a disperse XOSAN
|
||||
|
||||
You can grow a replicated XOSAN by adding extra disperse volumes, in other words a new disperse will be like in RAID 0 with the old one. It's a distributed-disperse type. Some examples:
|
||||
You can grow a replicated XOSAN by adding extra disperse volumes, in other words a new disperse will be like in RAID 0 with the old one. It's a **distributed-disperse** type. Some examples:
|
||||
|
||||
* To grow a disperse 3, you need 3 new nodes. You'll add the total capacity of each disperse to make a distributed-disperse on 2x3 dispersed nodes.
|
||||
* To grow a disperse 6, you need 6 new nodes.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@ Pros:
|
||||
|
||||
Cons:
|
||||
|
||||
* low capacity (so higher cost, better for SSDs)
|
||||
* lower capacity (so higher cost, better for SSDs)
|
||||
* a bit more complex to maintain in distributed-replicated (see "RAID 10 like")
|
||||
|
||||
### 2-way replication
|
||||
@@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ Same than 2-way, but data is replicated on 3 nodes in total.
|
||||
|
||||
### Building a "RAID 10" like
|
||||
|
||||
If you have more than 2 or 3 nodes, it could be interesting to distribute data on multiple replicated nodes. This is called "distributed-replicated" type. Here is an example with 6 nodes:
|
||||
If you have more than 2 or 3 nodes, it could be interesting to **distribute** data on multiple replicated nodes. This is called "**distributed-replicated**" type. Here is an example with 6 nodes:
|
||||
|
||||
![picture distributed-replicated with 6 nodes]()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ In order to work, XOSAN need a minimal set of requirements.
|
||||
|
||||
## Storage
|
||||
|
||||
XOSAN is deployed on an existing **Local LVM storage**, that XenServer configure by default during its installation. However, you can create yourself easily this kind of storage while using Xen Orchestra:
|
||||
XOSAN can be deployed on an existing **Local LVM storage**, that XenServer configure by default during its installation. However, you can also create yourself easily this kind of storage while using Xen Orchestra:
|
||||
|
||||
* Go on the "New" menu entry, then select "Storage"
|
||||
* Select the host having the disk you want to use for XOSAN
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ XOSAN will use the network card you choose at creation. For better performances,
|
||||
|
||||
## RAM
|
||||
|
||||
Each XOSAN VM deployed will use 2GiB of RAM. It could be increased (sweet spot seems to be around 4GiB), but it's also workload and infrastructure related. If you don't have a lot of RAM, keep it to 2GiB. If RAM is not an issue, 4GiB is better.
|
||||
Each XOSAN VM will use 2GiB of RAM. It could be increased (sweet spot seems to be around 4GiB), but it's also workload and infrastructure related. If you don't have a lot of RAM, keep it to 2GiB. If RAM is not an issue, 4GiB is better.
|
||||
|
||||
## CPU
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ There is 2 modes for creating an XOSAN storage. They are different and the choic
|
||||
|
||||
That's why it's **very important to understand pros and cons** of each type.
|
||||
|
||||
> On "top" of there 2 types, you can also deciding to spread all operations to multiple number of volumes. This is called **distributed** mode. It's very similar to *RAID 0*, which can be placed on top of a *RAID 1* for example. We'll talk about it in the end of this guide.
|
||||
> On "top" of there 2 types, you can also decide to spread all operations to multiple number of volumes. This is called **distributed** mode. It's very similar to *RAID 0*, which can be placed on top of a *RAID 1* for example. We'll talk about it in the end of this guide.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is those 2 types:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user