2.1 KiB
CloudInit
CloudInit support is available from 4.11 release
Cloud-init is a program "that handles early initialization of a cloud instance"[^n]. In other words, you can, on a "cloud-init"-ready template VM, pass a lot of data at first boot:
- setting hostname
- add ssh keys
- grow automatically the file system
- create users
- and a lot more!
This tool is pretty standard and used everywhere. A lot of existing cloud templates are using it.
So it means customizing very easily your VM when you create it from a compatible template. It brings you closer to the "instance" principle, like in Amazon cloud or OpenStack.
Requirement
You only need to use a template of a VM with CloudInit installed inside it. Check this blog post to learn how to install CloudInit.
Usage
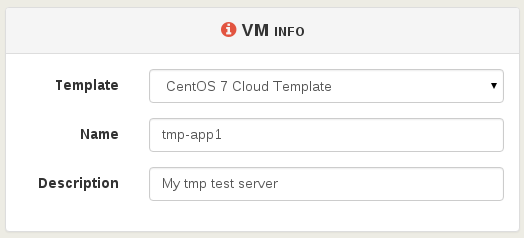
First, select your compatible template (CloudInit ready) and name it:
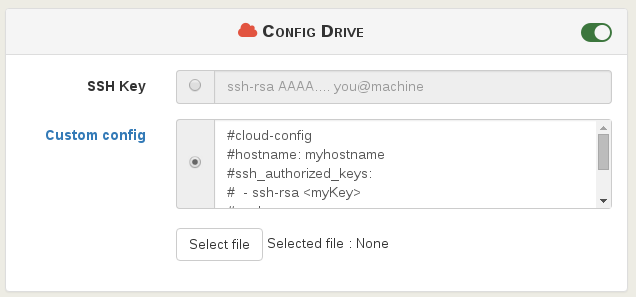
Then, activate the config drive and put your SSH key. Or you can also use a custom CloudInit configuration:
CloudInit configuration examples are available here.
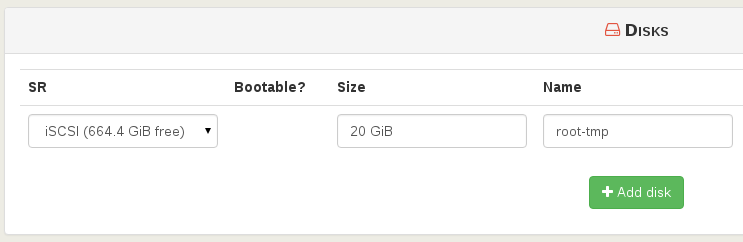
You can extend the disk size (in this case, the template disk was 8 GiB originally):
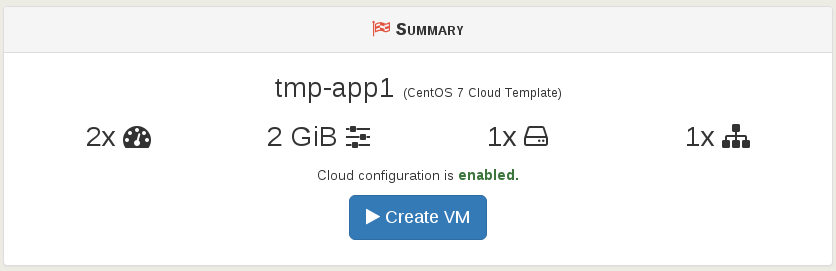
Finally, create the VM:
Now start the VM and SSH on its IP:
- the system got the right VM hostname (from VM name)
- you don't have to use a password to access it (thanks to your SSH key):
$ ssh centos@192.168.100.226
[centos@tmp-app1 ~]$
The default cloud-init configuration could allow you to be to be a sudoer directly:
[centos@tmp-app1 ~]$ sudo -s
[root@tmp-app1 centos]#
Check the root file system size: indeed, it was automatically grown to what you need:
[centos@tmp-app1 ~]$ df -h
/dev/xvda1 20G 1,2G 18G 6% /